In the fast-paced world of product development, where user expectations are constantly evolving, the foundational work of understanding exactly what users need and desire can make or break a project. Many teams rush into design and development, only to find themselves backtracking, redesigning, and overspending because critical user experience (UX) requirements were either missed, misunderstood, or poorly communicated. This common pitfall underscores the immense value of a structured approach to defining the user experience from the outset.
Imagine a blueprint for a house: without detailed architectural plans, builders would struggle to create a functional, aesthetically pleasing, and safe home. Similarly, in UX design, a robust system for collecting and documenting user needs acts as that essential blueprint. It’s not just about listing features; it’s about delving deep into user behaviors, motivations, pain points, and aspirations to craft truly impactful digital experiences. This structured approach benefits everyone involved, from product managers and designers to developers and stakeholders, ensuring alignment and a shared vision.
Why a Structured Approach to UX Requirements Matters
The journey from concept to a successful digital product is fraught with potential miscommunications and assumptions. Without a clear and documented set of user experience requirements, teams often work in silos, leading to feature creep, scope changes, and ultimately, a product that fails to resonate with its intended audience. A systematic method for gathering UX needs minimizes these risks by providing a single source of truth for all user-centric decisions. It’s about building a shared understanding across diverse teams.
This dedicated effort ensures that the user remains at the heart of every design choice. It moves the conversation beyond "what features do we want?" to "what problems are we solving for our users, and how will our design facilitate that?" By formalizing the elicitation of user insights, organizations can reduce costly rework cycles, accelerate development timelines, and significantly improve user satisfaction and product adoption rates. It’s an investment that pays dividends throughout the product lifecycle.
The Core Components of an Effective UX Requirements Gathering Process
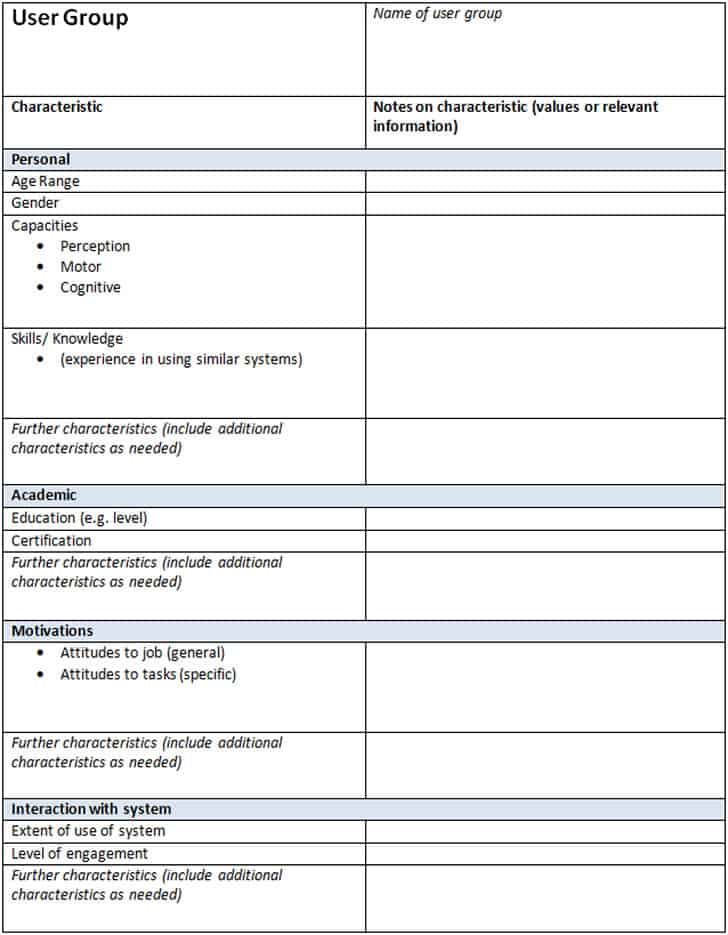
Creating a comprehensive collection of user experience requirements involves more than just jotting down ideas; it demands a systematic approach that captures various facets of the user and their interactions with the product. An effective requirements elicitation framework typically synthesizes insights from multiple sources, transforming raw data into actionable design specifications. This ensures that every aspect of the user journey is considered and documented.
A robust process for gathering UX needs often includes the following key elements:
- **Project Goals and Objectives:** Clearly defining what the product aims to achieve for both the business and the user. What problems will it solve, and what value will it deliver?
- **User Personas:** Detailed profiles of target users, including their demographics, behaviors, motivations, goals, and pain points. These help teams empathize with their users.
- **User Stories/Scenarios:** Short, simple descriptions of a feature from the perspective of an end-user. They follow the format “As a [type of user], I want [some goal] so that [some reason].” Scenarios provide narrative context.
- **Functional Requirements (User-Facing):** What the system *must do* to meet user needs. These often describe specific features or actions users can take.
- **Non-Functional Requirements (User-Impacting):** Qualities of the system like performance, usability, accessibility, and security that affect the user experience but aren’t specific features.
- **Information Architecture (IA):** How content and functionality will be organized and structured within the product to ensure intuitive navigation and findability.
- **User Flows/Journey Maps:** Visualizations of the steps a user takes to complete a task or achieve a goal within the product. These highlight potential friction points.
- **Content Requirements:** Specifications for the type, tone, and amount of content needed, including text, images, and multimedia elements.
- **Usability Metrics and Success Criteria:** Measurable benchmarks to determine if the design effectively meets user needs and business objectives. How will we know if we succeeded?
- **Technical Constraints and Opportunities:** Understanding the limitations and possibilities imposed by technology, which can influence design choices.
Strategies for Successful Requirements Elicitation
Eliciting user needs isn’t a passive activity; it requires proactive engagement and a mix of research methods. The success of your user experience requirements collection hinges on your ability to extract meaningful insights from various stakeholders and users. No single method will capture all necessary information, so a blended approach is often most effective.
One of the most powerful strategies is direct user research. This includes conducting user interviews to understand individual perspectives, running usability tests on existing products or prototypes to observe behaviors, and deploying surveys to gather quantitative data from a broader audience. Contextual inquiry, where researchers observe users in their natural environment, can reveal unspoken needs and workarounds that interviews might miss. Stakeholder interviews are equally crucial for aligning business goals with user needs. Workshops with cross-functional teams can also foster collaboration and unearth hidden requirements or assumptions. Regularly reviewing existing analytics data and customer support tickets can provide valuable insights into current pain points and usage patterns, guiding the direction of your design requirements checklist.
Leveraging Your Requirements for Design and Development
Once your user experience requirements are meticulously documented, their true value comes to fruition in guiding the design and development phases. These detailed specifications act as a North Star, ensuring that every design decision and line of code directly contributes to solving user problems and achieving product goals. It’s the bridge between understanding “what” users need and creating “how” the product will deliver it.
Designers use these defined user experience expectations to create wireframes, prototypes, and visual designs that are grounded in actual user needs rather than subjective preferences. Developers, in turn, can build with confidence, knowing that the features they implement are directly tied to documented user requirements, reducing guesswork and rework. This continuous reference to the initial user research outputs also facilitates more effective quality assurance and testing, as testers can validate features against explicit user stories and success criteria. Ultimately, a well-defined set of user-centered design requirements fosters a cohesive development process and a product that truly delights its users.
Customizing Your Template for Diverse Projects
While a standard approach for gathering UX needs offers a solid foundation, its true power lies in its adaptability. Not all projects are created equal; a small feature enhancement will have different requirements than an entirely new product launch or a complex enterprise system. The beauty of a robust requirements elicitation framework is that it’s a living document, meant to be tailored.
For smaller projects, you might streamline certain sections, focusing only on the most critical user stories and functional requirements. For highly innovative or experimental products, emphasis might shift towards more extensive user research and iterative prototyping, with requirements evolving alongside user feedback. Enterprise solutions, conversely, might demand more rigorous documentation around security, accessibility, and integration challenges. The key is to understand your project’s scope, complexity, and unique user base, then selectively apply the elements that will provide the most value without creating unnecessary overhead. This flexibility ensures that your system for collecting UX data remains a practical tool, not a bureaucratic burden.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the primary benefit of a Ux Requirements Gathering Template?
The primary benefit is establishing a shared understanding of user needs and product goals across all stakeholders and teams. It minimizes assumptions, reduces costly rework, and ensures the final product is truly user-centered, leading to higher user satisfaction and adoption.
Who should be involved in the UX requirements gathering process?
A diverse group should be involved, including product managers, UX designers, researchers, developers, business analysts, and most importantly, end-users. Stakeholders from sales, marketing, and customer support can also provide valuable insights into user pain points and market opportunities.
How often should UX requirements be revisited or updated?
UX requirements should be revisited regularly throughout the product lifecycle, especially during iterative development cycles (e.g., Agile sprints), after user testing, or when new market insights emerge. They are living documents that evolve as understanding of the user and product matures.
Can a single Ux Requirements Gathering Template apply to all types of projects?
While a core framework can be adapted, a single template rarely fits all project types without customization. The best approach is to have a flexible template that can be scaled up or down, adding or removing sections based on the project’s scope, complexity, and specific needs, such as a new product launch versus a feature update.
What is the difference between functional and non-functional UX requirements?
Functional requirements describe what the system *does* to meet user needs (e.g., “The user can add items to a shopping cart”). Non-functional requirements describe *how well* the system performs its functions, impacting the user experience indirectly (e.g., “The shopping cart page must load within 2 seconds”). Both are critical for a positive user experience.
Implementing a robust user experience requirements collection system is more than just a checklist; it’s a fundamental shift towards a more user-centric and efficient product development paradigm. It transforms ambiguous ideas into concrete, actionable insights that guide every step of the design and development journey. By investing time upfront in meticulously defining user needs and translating them into clear requirements, organizations pave the way for creating digital products that not only meet business objectives but also genuinely resonate with and empower their users.
Embrace the power of structured user experience requirements to build products that not only look good but perform exceptionally, truly solving real-world problems. This proactive approach fosters collaboration, reduces risks, and ultimately leads to more successful, sustainable, and beloved digital experiences. Start crafting your comprehensive user-centered design requirements today and watch your projects thrive.