In California’s diverse and often intensely hot climate, protecting outdoor workers from the debilitating and potentially fatal effects of heat illness isn’t just a best practice – it’s a legal imperative. Employers across various sectors, from agriculture and construction to landscaping and utilities, face the critical challenge of ensuring their workforce remains safe when temperatures soar. The stakes are incredibly high, encompassing not only the well-being of employees but also significant regulatory penalties, reputational damage, and lost productivity for businesses that fall short.
Navigating the intricacies of Cal/OSHA’s Title 8, Section 3395 Heat Illness Prevention standard can seem daunting, especially for businesses with limited resources or those new to compliance. This is where a well-structured and comprehensive program becomes an indispensable tool. It transforms complex regulations into actionable steps, providing a clear roadmap for safeguarding employees and meeting your legal obligations.
Understanding the Imperative: Why Heat Illness Prevention Matters
The human body is remarkably resilient, but its ability to regulate temperature under extreme heat stress has limits. When working outdoors in hot environments, individuals can quickly succumb to heat cramps, heat exhaustion, and, most dangerously, heat stroke. These conditions are not mere discomforts; they are serious medical emergencies that can lead to permanent organ damage or even death if not addressed promptly and effectively.
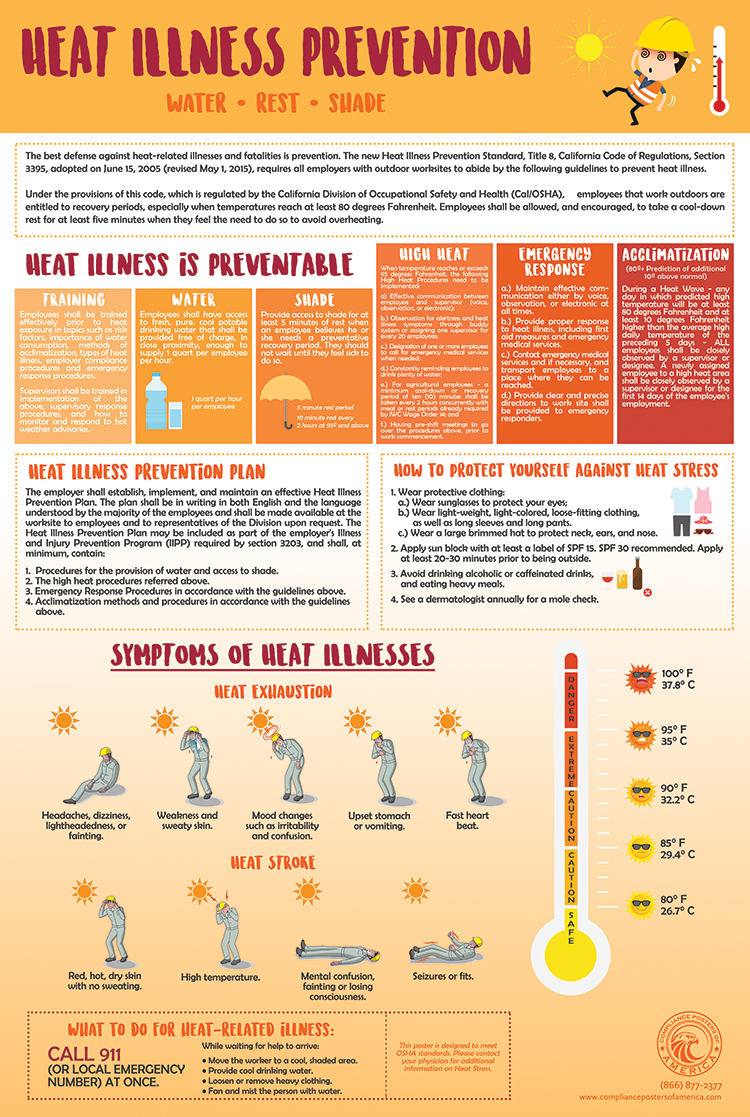
Cal/OSHA’s Heat Illness Prevention standard is one of the most comprehensive in the nation, reflecting California’s proactive stance on worker safety. It mandates specific actions employers must take to prevent heat-related illness among outdoor workers. These requirements are not optional; they are legally binding and subject to rigorous enforcement, underscoring the profound importance of a robust workplace heat prevention strategy.
Beyond legal compliance, a strong commitment to preventing heat-related illness fosters a positive workplace culture. Employees who feel their safety is a priority are generally more engaged, productive, and loyal. Conversely, neglecting heat safety can erode trust, lead to high turnover, and significantly impact morale, creating a ripple effect throughout the organization.
The Core Elements of a Robust Heat Illness Prevention Plan
A truly effective heat illness prevention program is built upon several foundational pillars, each designed to proactively mitigate risks and respond effectively when incidents occur. These elements are interconnected, forming a comprehensive safety net for outdoor workers. Understanding these core components is the first step toward developing or enhancing your own workplace heat safety protocols.
At its heart, any prevention plan must clearly define roles and responsibilities, ensuring that everyone from top management to frontline supervisors and employees understands their part in maintaining a safe environment. It also requires a systematic approach to identifying and evaluating heat hazards, implementing controls, and continuously monitoring conditions. This proactive stance is crucial for adapting to varying weather conditions and work demands.
Key to the program’s success is also the provision of adequate resources. This includes not just water and shade, but also appropriate training, emergency response procedures, and acclimatization protocols. These resources empower workers to stay safe and enable supervisors to make informed decisions that prioritize health above all else.
Leveraging a Program Template: Your Path to Compliance and Safety
Developing a comprehensive heat illness prevention program from scratch can be a time-consuming and resource-intensive endeavor. This is precisely where a high-quality Cal Osha Heat Illness Prevention Program Template proves invaluable. Such a template provides a structured, pre-formatted framework that meticulously covers all the required elements of Cal/OSHA’s standard. It acts as a guide, ensuring no critical component is overlooked and that your resulting program is fully compliant.
The primary benefit of utilizing a prevention program template is efficiency. Instead of spending countless hours drafting policies and procedures, you can focus on tailoring the existing framework to your specific operational needs. This significantly reduces the administrative burden, allowing businesses to implement a robust heat safety program more quickly and effectively. It’s a practical tool designed to streamline the journey to full regulatory adherence.
Furthermore, a well-designed template often includes best practices and clear language, making complex regulatory requirements more accessible and understandable for employers and employees alike. It serves as an educational resource in itself, highlighting areas that demand particular attention and guiding users toward a comprehensive and actionable workplace heat prevention strategy.
Key Components to Customize in Your Prevention Program
While a program framework provides an excellent foundation, it’s crucial to remember that it’s a "template" – meaning it requires customization to truly fit your specific workplace. Every business, every job site, and every work crew is unique. Tailoring the generic framework ensures that your heat illness prevention plan is not just compliant on paper, but genuinely effective in practice.
Here are the critical areas you will need to personalize within any Cal/OSHA heat illness prevention program:
- Company-Specific Information: Insert your company’s official name, contact information, and specific job site locations. Ensure emergency contacts and local medical facility details are accurate and current for each operational area.
- Designated Responsible Persons: Clearly identify the individuals or roles responsible for implementing and overseeing the heat illness prevention plan. This includes supervisors, safety managers, and designated personnel for emergency response.
- Specific Job Hazards and Controls: Detail the particular heat hazards present in your work environment (e.g., direct sun, radiant heat, strenuous activity) and the specific control measures you will implement, such as engineering controls, administrative controls, and personal protective equipment.
- Water Provision Protocols: Outline the exact methods for providing fresh, pure, and suitably cool drinking water. Specify locations, frequency of replenishment, and procedures for ensuring sufficient quantities are always available, considering the number of employees and work intensity.
- Shade Access Rules: Describe the specific types of shade provided (e.g., canopies, tents, vehicles), where it will be located, and how workers will be ensured access to it for mandatory cool-down rests and breaks. Include provisions for mobile operations.
- High-Heat Procedures: Detail the heightened precautions that will be taken when temperatures reach 95°F or higher. This includes more frequent breaks, mandatory observation of employees, and communication protocols.
- Emergency Response Plan: Customize the emergency procedures for heat-related illness. Include clear steps for recognizing symptoms, initiating first aid, calling for medical assistance, and transporting affected employees. List specific phone numbers and nearest clinic information.
- Acclimatization Schedule: If applicable, detail your plan for gradually increasing new employees’ or returning employees’ exposure to heat, allowing their bodies to adjust safely over a period of time.
- Training Content and Schedule: Specify the exact content of your heat illness prevention training, who will conduct it, and how often it will be provided to employees and supervisors. Include methods for documenting training completion.
- Communication Methods: Describe how information about the prevention program, current heat conditions, and emergency procedures will be communicated to all employees, including those with limited English proficiency.
Implementing Your Heat Illness Prevention Strategy
Once your customized heat illness prevention plan is complete, the next crucial step is effective implementation. A beautifully written document means little if it’s not put into action on the ground. This involves a commitment from all levels of the organization to actively promote and adhere to the established protocols.
Begin by disseminating the customized prevention program to all relevant personnel, especially supervisors and team leads. These individuals are on the front lines and must be fully conversant with every aspect of the plan. Ensure they understand their responsibilities regarding providing water, shade, and monitoring workers for signs of heat stress.
Regular checks and balances are vital. Supervisors should routinely verify that water is readily available and cool, shade is accessible, and employees are taking their required breaks. It’s also important to observe workers for any signs of discomfort or heat illness and to encourage open communication about how individuals are feeling in the heat.
Training and Communication: The Human Element
No heat illness prevention plan, however perfectly crafted, can succeed without effective training and continuous communication. Employees and supervisors must not only be aware of the program’s existence but also fully understand its content and their role within it. This is where the human element of safety truly comes into play.
Comprehensive training for all outdoor employees is a mandatory component of Cal/OSHA’s standard. This training must cover the signs and symptoms of heat illness, the importance of water and shade, the employer’s procedures, and how to report symptoms or concerns. Supervisors require additional training on how to respond to emergencies, implement high-heat procedures, and identify and address risk factors. Training should be interactive and accessible, particularly for employees with diverse language backgrounds.
Beyond formal training sessions, ongoing communication is essential. This can include daily briefings on expected temperatures and specific precautions for the day, safety posters in multiple languages, and regular reminders about hydration and breaks. Creating an environment where employees feel comfortable reporting early symptoms of heat stress without fear of reprisal is paramount. This open dialogue helps catch potential issues before they escalate into serious medical emergencies.
Beyond the Template: Continuous Improvement
A heat illness prevention program is not a static document to be filed away once completed. It is a living, breathing framework that requires continuous review, evaluation, and improvement. The outdoor work environment is dynamic, with changing weather patterns, new work processes, and evolving workforce demographics, all of which necessitate an adaptable approach to safety.
Regularly review incident reports, near-misses, and feedback from employees to identify areas where the prevention program could be strengthened. Conduct annual reviews, or more frequently if significant changes occur in your operations or if you experience a heat-related incident. Adjust your water provision, shade strategies, or training content based on lessons learned and emerging best practices.
Engaging employees in this review process can yield invaluable insights. They are the ones directly experiencing the heat and applying the safety protocols, making their perspectives crucial for effective improvements. A commitment to continuous improvement ensures your workplace heat safety strategy remains robust, responsive, and ultimately, life-saving.
In California’s demanding outdoor work environments, a proactive approach to heat illness prevention is not merely a regulatory obligation but a fundamental ethical responsibility. Leveraging a comprehensive framework like a Cal Osha Heat Illness Prevention Program Template provides an indispensable starting point, offering the structure and guidance needed to build a fully compliant and highly effective safety program. It empowers employers to quickly establish robust protocols, transforming complex legal mandates into clear, actionable steps that safeguard worker health and well-being.
By customizing the template to your specific operations, diligently implementing the program, and fostering a culture of continuous safety awareness and improvement, you can create a workplace where employees are protected even under the harshest conditions. This proactive investment in safety not only shields your business from legal repercussions but, more importantly, ensures that every worker returns home safely at the end of the day, contributing to a healthier and more productive workforce across the Golden State.