In the intricate world of software development and project management, clarity is not just a virtue—it’s an absolute necessity. Projects often face hurdles not due to a lack of effort or skill, but from a fundamental misalignment in understanding what needs to be built. Stakeholders, developers, and testers might all operate with slightly different interpretations of the desired outcome, leading to costly reworks, missed deadlines, and ultimately, a product that doesn’t quite hit the mark.
This is where a structured approach to defining and tracking requirements becomes invaluable, transforming ambiguity into actionable insights. A robust tool that ensures everyone is on the same page, from initial concept to final deployment, can be the difference between a project’s success and its struggle. It serves as the single source of truth, guiding development and ensuring every functional aspect of a system is precisely understood and accounted for.
The Imperative of Clarity in Software Development
Developing any new product or system is a journey fraught with potential miscommunications. Requirements, the very foundation upon which development is built, are often dynamic and can evolve throughout the project lifecycle. Without a clear, centralized method for documenting, tracking, and managing these changes, teams can quickly lose sight of the project’s true scope and objectives.
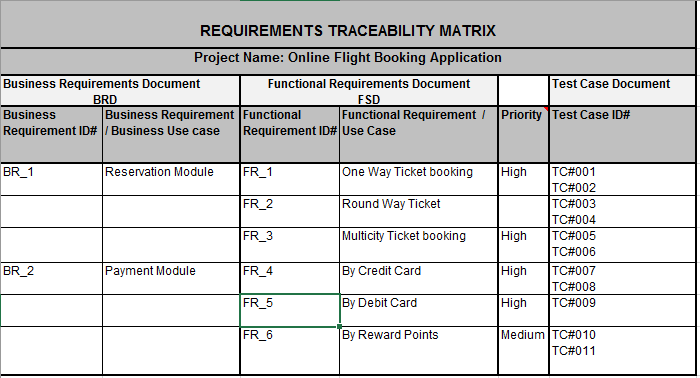
This lack of traceability can lead to a host of problems: features implemented incorrectly, critical functionalities overlooked, and user expectations unmet. It underscores the profound need for a systematic tool that not only captures what needs to be done but also links it to design, development, and testing efforts. Such a tool ensures that every piece of the puzzle contributes to the final vision.
What Exactly is a Requirements Traceability Matrix?
At its core, a requirements traceability matrix is a document that maps and traces requirements throughout the project lifecycle. While often simply referred to as a requirements matrix, its full name, a traceability matrix, highlights its primary purpose: to demonstrate the links between different requirements, and between requirements and other artifacts like test cases, design specifications, and business objectives. It typically uses a grid format, providing a clear visual representation of these interdependencies.
This powerful document acts as a living record, ensuring that every functional requirement, non-functional requirement, and business rule is explicitly documented and linked to its origins and its verification. It answers critical questions like "Why are we building this feature?" and "How will we test it?" by systematically connecting the dots. The functional requirements matrix template serves as a pre-built framework to streamline this essential process, making it easier for teams to adopt and adapt.
The Unquestionable Benefits of Employing a Requirements Matrix
Implementing a comprehensive requirements matrix offers a multitude of advantages that extend across the entire project team and lifecycle. Its value lies in its ability to bring structure, transparency, and accountability to even the most complex projects.
- **Enhanced Clarity and Understanding:** It provides a **single, unified view** of all requirements, ensuring that every team member, from business analysts to developers and testers, shares a common understanding. This minimizes misinterpretations and assumptions.
- **Improved Scope Management:** By clearly outlining what is (and isn’t) in scope, a requirements matrix helps to prevent **scope creep**. Any new request can be evaluated against existing requirements and the matrix updated accordingly, with clear implications.
- **More Effective Test Coverage:** Each requirement can be directly linked to one or more test cases. This ensures that **every specified function** is thoroughly tested, improving the quality and reliability of the final product.
- **Easier Impact Analysis:** When a requirement changes, the matrix instantly reveals which other requirements, design elements, or test cases might be affected. This allows for **proactive impact assessment** and better change management.
- **Better Risk Mitigation:** Identifying missing links or areas of weak traceability can highlight potential risks early in the project. This enables teams to address issues **before they escalate**, saving time and resources.
- **Streamlined Communication:** It serves as a central reference point for discussions and decisions, fostering **efficient communication** among all stakeholders and reducing the need for endless meetings to clarify details.
- **Regulatory Compliance and Audit Trails:** For projects in regulated industries, a robust requirements traceability matrix provides an **invaluable audit trail**, demonstrating how requirements were met and verified, which is crucial for compliance.
Key Components of an Effective Requirements Matrix Template
While specific fields may vary based on project type and organizational needs, a well-designed functional requirements matrix template typically includes several core elements. These components ensure comprehensive documentation and effective traceability.
- Unique ID: A distinct identifier for each requirement (e.g., FR001, NF005). This is crucial for easy referencing and tracking.
- Requirement Description: A clear, concise statement detailing what the system must do. This should be unambiguous and testable.
- Source/Origin: Who requested the requirement or where it originated (e.g., specific stakeholder, business rule, regulatory standard).
- Priority: A ranking (e.g., High, Medium, Low, Must-Have, Should-Have) indicating the importance of the requirement.
- Status: The current state of the requirement (e.g., Drafted, Approved, Implemented, Tested, Deferred, Canceled).
- Owner: The person responsible for the requirement’s definition and management.
- Associated Use Cases/User Stories: Links to related use cases or user stories that elaborate on the requirement’s context and user interaction.
- Design Specification Link: Reference to the design document or section that addresses how this requirement will be implemented.
- Test Case ID(s): The identifier(s) of the test cases designed to verify this specific requirement. This is critical for ensuring full test coverage.
- Verification Method: How the requirement will be verified (e.g., User Acceptance Testing, Automated Testing, Inspection).
- Comments/Notes: Any additional information, clarifications, or historical context relevant to the requirement.
How to Leverage and Customize Your Requirements Matrix
Adopting a requirements management tool doesn’t mean a rigid, one-size-fits-all approach. Its true power lies in its adaptability. Once you have a base template, tailoring it to your specific project needs is essential for maximizing its effectiveness.
Start by reviewing the default columns in your chosen requirements specification template. Consider what information is genuinely critical for your team and stakeholders. For instance, a highly regulated project might need additional fields for legal compliance or specific security categorizations, whereas a smaller, agile project might streamline it to focus on core user stories and their acceptance criteria. Add or remove columns to reflect the unique aspects of your development process, such as "Module," "Release Version," or "Acceptance Criteria." The goal is to make the document work for you, not the other way around.
Best Practices for Implementing Your Functional Requirements Template
To truly harness the power of a requirements tracking sheet, simply filling it out isn’t enough. Effective implementation requires discipline and a commitment to best practices throughout the project lifecycle.
- **Start Early, Maintain Continuously:** Begin populating your requirements management tool as soon as requirements are gathered, and update it regularly. It’s a **living document**, not a one-time setup.
- **Define Clear Responsibility:** Assign a **single owner** for the maintenance and accuracy of the requirements matrix. This ensures accountability and consistency.
- **Keep Descriptions Concise and Unambiguous:** Each requirement description should be clear, testable, and **avoid jargon** where possible. Break down complex requirements into smaller, manageable pieces.
- **Establish Linkages Explicitly:** Ensure all requirements are properly linked to their sources, design elements, and test cases. **Incomplete links** reduce the value of traceability.
- **Version Control Your Matrix:** Treat your requirements traceability matrix like any other project artifact. Use **version control** to track changes over time, allowing for rollbacks if necessary.
- **Involve Stakeholders:** Regularly review the functional specification matrix with relevant stakeholders to ensure it accurately reflects their needs and expectations. **Early feedback** is invaluable.
- **Integrate with Other Tools:** Where possible, integrate your requirements matrix with other project management, development, and testing tools. This can automate updates and **reduce manual effort**.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a Functional Requirements Matrix and a Requirements Traceability Matrix?
While often used interchangeably, a Functional Requirements Matrix specifically focuses on detailing “what” the system should do, capturing all functional behaviors. A Requirements Traceability Matrix is a broader concept that maps all types of requirements (functional, non-functional, business) to other project artifacts like design documents, test cases, and business objectives, ensuring a comprehensive link across the project lifecycle. A functional requirements matrix can be a component or a specific application of a broader traceability matrix.
Who is typically responsible for maintaining the requirements matrix?
The primary responsibility for maintaining the requirements matrix often falls to the Business Analyst (BA) or Product Owner. However, it’s a collaborative effort. Project Managers ensure its use, developers reference it for implementation, and testers use it to build test cases. The owner usually coordinates input and ensures its accuracy and completeness.
Can a spreadsheet program be used as a requirements matrix template?
Absolutely. For many projects, especially smaller ones, a well-structured spreadsheet program (like Excel or Google Sheets) can serve as an effective requirements tracking sheet. It allows for custom columns, filtering, and basic linking. For larger, more complex projects or those requiring advanced features like automated reporting, dedicated requirements management software might be more suitable.
How does a requirements matrix help with agile development?
In agile environments, a requirements matrix, often adapted to track user stories and their acceptance criteria, helps maintain clarity and focus. It ensures that each user story is linked to specific features and test cases, promoting test-driven development and providing a clear path from business need to delivered functionality. It also helps manage dependencies between stories and assess the impact of changes within sprints.
Is it necessary to have a requirements matrix for every project?
While extremely beneficial for nearly all projects, the complexity and formality of a requirements matrix can be scaled to fit project size and organizational needs. For very small, short-term projects with minimal risk, a simplified version might suffice. However, for projects with multiple stakeholders, regulatory compliance needs, or significant complexity, a well-maintained requirements matrix is invaluable for ensuring success and mitigating risks.
Embracing a robust requirements matrix template is more than just good documentation; it’s a strategic investment in project success. It transforms abstract ideas into concrete, traceable deliverables, fostering a shared vision and reducing the likelihood of costly errors. By providing a clear roadmap from inception to delivery, it empowers teams to build precisely what is needed, on time and within budget.
As your projects evolve and grow in complexity, the value of a meticulously managed requirements traceability matrix will only become more apparent. It’s the silent hero behind seamless execution, ensuring every functional requirement is not just met, but demonstrably fulfilled. Start leveraging this powerful tool today to bring unparalleled clarity and control to your development lifecycle.