In the intricate dance of industrial operations, where powerful machinery and complex energy sources are commonplace, safety is not merely a priority—it’s an absolute imperative. The potential for unexpected machine startup or the release of stored energy can transform routine maintenance into a life-threatening situation in mere seconds. This is precisely where a robust hazardous energy control program, commonly known as Lockout/Tagout (LOTO), becomes the bedrock of workplace safety. It’s the critical safeguard that protects workers from severe injuries or fatalities while servicing or maintaining equipment.
Developing and implementing an effective LOTO program can feel like a daunting task for many organizations. OSHA’s standard (29 CFR 1910.147) lays out stringent requirements, demanding a detailed, written program tailored to specific equipment and procedures. For many, the concept of an Osha Lockout Tagout Program Template serves as an invaluable starting point, offering a structured framework to ensure compliance and, most importantly, protect human lives. This article will delve into the essence of such a template, its benefits, and how it can be customized to forge a truly resilient safety culture within your organization.
The Unseen Danger: Why Lockout/Tagout is Non-Negotiable
Imagine a scenario where a worker is performing routine maintenance inside a machine, unaware that a power source could be reactivated at any moment. Or consider the stored hydraulic pressure that could suddenly release, crushing a limb. These aren’t hypothetical horror stories; they are real risks that underscore the critical need for an energy control program. OSHA estimates that compliance with the LOTO standard prevents an estimated 120 fatalities and 50,000 injuries each year.
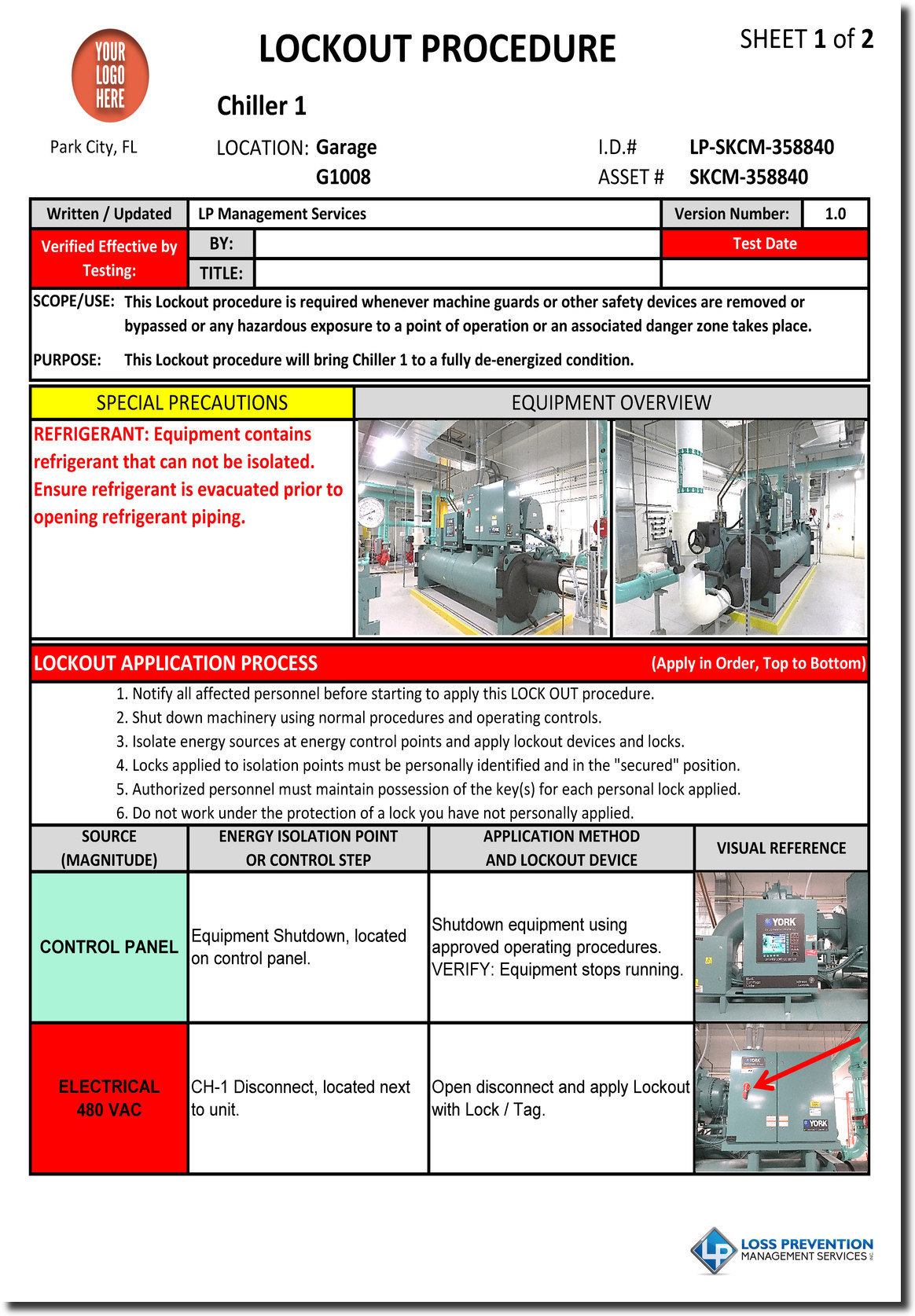
The core principle of lockout/tagout is simple yet profoundly effective: isolate and de-energize machinery and equipment before work begins, then apply a lock and a tag to prevent unexpected startup or release of stored energy. This process ensures that only the authorized person who applied the lock can remove it, thereby maintaining absolute control over the energy source during the task. Neglecting these procedures can lead to electrocutions, amputations, crush injuries, and other severe incidents that devastate lives and incur significant legal and financial consequences for businesses.
Decoding OSHA’s Lockout/Tagout Requirements
OSHA’s standard for The Control of Hazardous Energy (29 CFR 1910.147) is comprehensive, dictating specific requirements for employers to protect employees from hazardous energy during servicing and maintenance of machines and equipment. This standard mandates that employers establish an energy control program consisting of energy control procedures, employee training, and periodic inspections. It’s not enough to simply have locks and tags; a systematic approach is essential.
A key aspect of OSHA compliance is the requirement for specific written procedures for controlling hazardous energy. These procedures must detail the scope, purpose, authorization, rules, and techniques to be utilized for the control of hazardous energy, and the means to enforce compliance. Furthermore, the standard requires that all employees who operate, maintain, or service equipment be trained on the purpose and function of the energy control program. Periodic inspections of these procedures must also be conducted to ensure their effectiveness and compliance.
What Makes an Effective Lockout Tagout Program?
An effective lockout tagout program extends far beyond a binder full of paperwork; it’s a living document and a pervasive safety culture. It provides clear, actionable steps for every employee involved, ensuring that hazardous energy is properly controlled. Such a program not only meets regulatory requirements but also fosters a proactive safety environment where every individual understands their role in preventing accidents.
The true measure of an effective energy control program lies in its clarity, accessibility, and the consistency of its application. It should be easy for employees to understand and follow, leaving no room for ambiguity when lives are on the line. Beyond preventing incidents, a well-implemented program can also improve operational efficiency by standardizing maintenance procedures and reducing unexpected downtime related to safety incidents. It establishes a clear chain of command and responsibility, streamlining the entire safety process.
Building Your Foundation: Key Elements of a Comprehensive LOTO Program
Leveraging an initial framework, such as an Osha Lockout Tagout Program Template, can dramatically simplify the process of developing a comprehensive hazardous energy control program. While a template provides the skeletal structure, the muscle and organs of the program come from customizing it to your specific operations. A robust program must include several critical components, each meticulously designed to address specific aspects of energy control.
These elements work in concert to create a robust defense against hazardous energy, ensuring every potential risk is accounted for.
- **Energy Control Procedures:** Detailed, machine-specific instructions for safely shutting down, isolating, blocking, and securing machines or equipment to control hazardous energy. These procedures must identify specific hazardous energy sources and steps for **verification** of de-energization.
- **Employee Training:** Comprehensive training for all affected, authorized, and other employees. **Authorized employees** are those who perform the lockout or tagout, while **affected employees** are those who operate or work near the equipment being serviced.
- **Periodic Inspections:** Regular reviews of the energy control procedures and training to ensure they remain effective and compliant. These inspections must be performed at least **annually** by an authorized employee other than the one utilizing the procedure being inspected.
- **Lockout/Tagout Devices:** Providing and ensuring proper use of durable, standardized, identifiable, and substantial lockout and tagout devices. These devices must be **singly identifiable** and indicate the identity of the employee applying the device.
- **Program Administration:** Clear assignment of roles, responsibilities, and accountability for the program’s implementation and enforcement. This includes procedures for **shift changes** and contractor coordination.
- **Contractor Communication:** Procedures for informing outside contractors about your facility’s lockout/tagout procedures and ensuring their compliance. Clear communication prevents misunderstandings that could lead to **serious incidents**.
Customization is Key: Adapting Your LOTO Framework
While an initial LOTO program template offers an excellent starting point, its true value is realized through meticulous customization. No two workplaces are identical, and therefore, no generic program can fully address the unique hazardous energy risks present in every facility. The process of adapting this framework involves a thorough assessment of all machinery, equipment, and processes that could pose an energy hazard to employees.
This adaptation isn’t just about filling in blanks; it requires deep engagement with your operational specifics. You’ll need to identify every energy source (electrical, hydraulic, pneumatic, mechanical, thermal, chemical), understand how it can be isolated, and document the specific steps required for each piece of equipment. This machine-specific detail forms the core of your energy control procedures, ensuring that the guidelines are practical, relevant, and directly applicable to your operational environment. Involving the employees who actually perform the work is crucial in this phase, as their practical insights can refine procedures and foster greater buy-in.
Implementing and Sustaining Your Safety Culture
Implementation of an energy control program extends beyond merely documenting procedures; it requires a concerted effort to embed these practices into the daily fabric of your workplace culture. Initial training sessions are vital, but ongoing reinforcement and continuous improvement are what truly sustain the program’s effectiveness. Regular refresher training, toolbox talks, and visible management commitment are essential to keep safety front of mind.
Furthermore, a comprehensive LOTO program demands a system for managing change. When new machinery is introduced, old equipment is modified, or new processes are adopted, the energy control procedures must be reviewed and updated accordingly. Periodic audits and inspections, conducted by knowledgeable personnel, serve as critical checkpoints to ensure procedures are being followed correctly and that the program remains compliant with evolving OSHA standards. This proactive approach ensures that your commitment to safety is dynamic, adapting to new challenges and continuously striving for a safer work environment.
Embracing an Osha Lockout Tagout Program Template as a foundational tool can significantly streamline the creation of a robust and compliant hazardous energy control system. It provides a proven structure, allowing organizations to focus their resources on the critical details of customization and implementation. By methodically addressing each aspect of energy control, from detailed procedures to comprehensive training and ongoing audits, companies can dramatically reduce the risk of serious accidents and foster a culture where safety is paramount.
Ultimately, a diligently implemented and continuously refined lockout tagout program protects your most valuable asset: your employees. It demonstrates an unwavering commitment to their well-being, while simultaneously safeguarding your organization from the devastating repercussions of preventable incidents. Invest the time and resources now to build a program that not only meets regulatory standards but truly champions a secure and productive future for everyone.